According to the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP), solid waste generation is set to increase, from 2.1 billion tonnes in 2023 to 3.8 billion tonnes in 2025, and as organizations strive to meet sustainability targets, tackling this increase is fast becoming a priority—one that ESG hopes to tackle head on.
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals are a framework for evaluating an organization’s sustainability and ethical impact. However, aligning waste management systems with ESG requirements takes a forward-thinking approach and innovative solutions.
One way that organizations are looking to achieve better ESG is through smart waste management systems that aim to reduce waste generation and divert more waste away from landfill. Powered by technology, smart waste management helps to achieve ESG objectives while optimizing operations and cost-effectiveness, and here, we’ll explore how.
 Understanding ESG Goals and Waste Management
Understanding ESG Goals and Waste Management
Environmental, Social, and Governance goals serve as a framework for organizations to operate responsibly and sustainably. Here at RTS, we monitor and report our own ESG goals and how we progress towards them, but for those unfamiliar with this framework, the three pillars should guide businesses in minimizing environmental impact, fostering social responsibility, and ensuring strong ethical governance. This includes:
Environmental (E) — Focussing on sustainability efforts such as reducing carbon emissions, conserving resources, and managing waste efficiently, businesses that implement effective waste management strategies contribute to lowering pollution and promoting circular economies.
Social (S) — The social component emphasizes a company’s responsibility to its employees, communities, and stakeholders. Proper waste management supports public health, reduces environmental hazards, and promotes ethical supply chain practices.
Governance (G) — Governance ensures transparency, compliance, and ethical decision-making within an organization. Effective ESG strategies require leadership commitment, regulatory adherence, and responsible waste disposal policies.
 Achieving ESG Goals Through Smart Waste Management
Achieving ESG Goals Through Smart Waste Management
“Recycling is an important aspect of the waste management stream. We need to work smart, to make sure that it is sustainable and cost effective, and we’re working with the industry to do that.”
Sharon Kneiss, CEO of the National Waste and Recycling Association (NWRA)
Smart solutions are among the core pillars of our approach to waste management, and we see multiple avenues for technology to help your organization achieve your ESG goals.
For example, smart bin sensors, such as the Pello system, utilize digital sensors, tracking, and analytics. When the bin is full, a notification is sent, allowing for on-demand collection. In turn, the infrastructure behind the smart waste bin ensures optimization of routes so that trucks are on the road only when needed. Ultimately, this means fewer emissions and more efficient waste diversion.
However, smart waste management systems extend way beyond trash can sensors, encompassing the following:
Data-Driven Decision Making
Waste analytics platforms that provide unprecedented visibility into waste streams deliver a comprehensive view of waste generation and management. RTS is a pioneer in this field, and we have helped breweries, chain stores, stadiums, and more.
Circular Economy Integration
We are huge supporters of the circular economy, and our experience shows that adopting these principles in tandem with smart waste management systems can significantly improve diversion and reduce raw material costs.
Employee Engagement and Training
Employee and community participation is a big part of all ESG initiatives. Digital platforms that gamify waste reduction have been shown to increase community engagement, something we are exploring with our Cycle RVM (reverse vending machines).
Technology Implementation
Smart sensors, AI, and blockchain technology all have the potential to form the backbone of modern sustainable waste management, and we advise that any organization in getting smart waste management systems should be looking to these nascent technologies to improve ESG.
Integrating Smart Waste Management in ESG Strategies
Having advised numerous companies across a broad range of industries on how to improve their waste management systems, we suggest starting with the following steps when considering combining smart waste solutions with ESG goals.
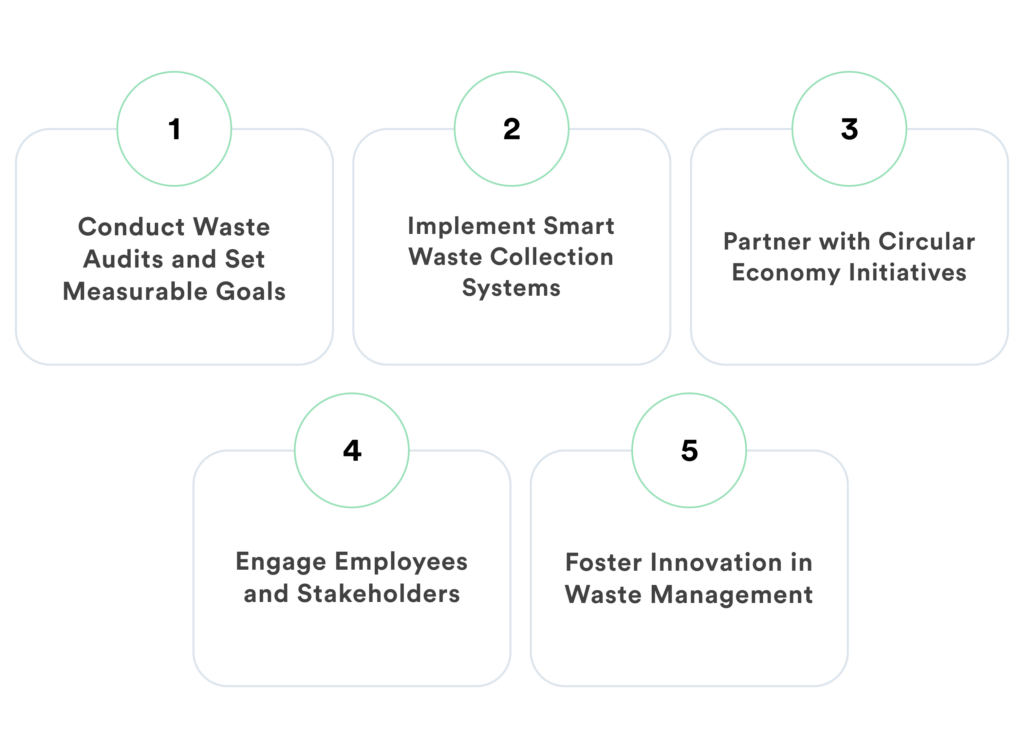
- Conduct Waste Audits and Set Measurable Goals
We always advise organizations to begin by conducting waste audits to assess waste generation patterns, identify inefficiencies, and set clear ESG-aligned targets for waste reduction and recycling. - Implement Smart Waste Collection Systems
Through our experience of instaling and monitoring IoT-enabled waste bins and collection systems, we often highlight to our client how they can help optimize pickup schedules to reduce fuel consumption and operational costs while improving overall efficiency. - Partner with Circular Economy Initiatives
Collaboration with circular economy stakeholders ensures waste materials are repurposed, reducing landfill impact and contributing to a sustainable supply chain. - Engage Employees and Stakeholders
Training programs, awareness campaigns, and incentive-based initiatives encourage employees and stakeholders to actively participate in sustainable waste management practices. We believe that education is key to increased engagement in any industry. - Foster Innovation in Waste Management
Encouraging research and development in waste management technologies helps businesses stay ahead in sustainability efforts. Investing in innovative solutions such as biodegradable materials, waste-to-energy systems, and AI-driven sorting methods enhances ESG impact.
 ESG Reporting and Transparency
ESG Reporting and Transparency
Among the most crucial aspects of ESG reporting is transparency, something that can build trust with investors, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies. Effective reporting ensures compliance, enhances corporate reputation, and drives informed decision-making. We suggest that aligning your goals with ESG reporting frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) is a good place to start.
The good news is that by utilizing advanced technologies like IoT sensors, AI analytics, and blockchain, organizations can collect and verify real-time data on waste production, disposal, and recycling efforts. This approach eliminates discrepancies and ensures the reliability of ESG reports.
On top of this, however, regular and transparent disclosures help stakeholders monitor progress and hold companies accountable for their ESG commitments. Publicly accessible reports foster trust and encourage continuous improvement in sustainability initiatives.
Transparent and accurate ESG reporting is crucial for organizations aiming to build trust with investors, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies. Effective reporting not only ensures compliance but also enhances corporate reputation and decision-making.
Future Trends in Smart Waste Management for ESG Achievement
Both the ESG frameworks and smart waste management sectors are fast-evolving fields, and we believe the future is bright for companies looking to combine the two.
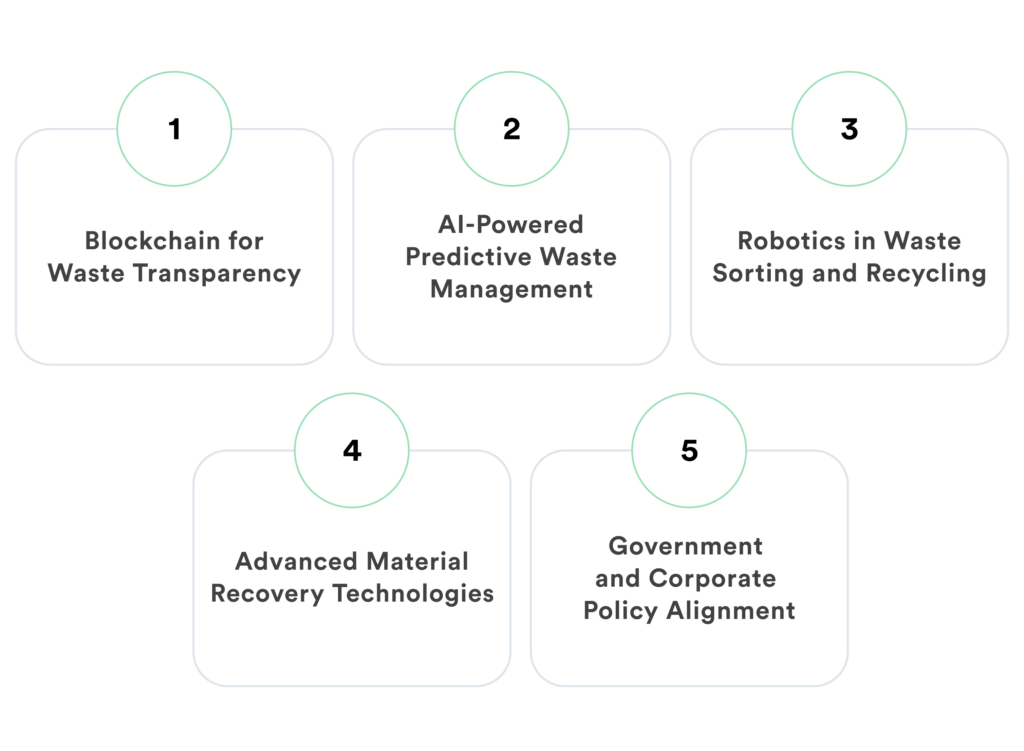
- Blockchain for Waste Transparency
Blockchain technology is being utilized to track waste transactions securely, ensuring transparency and traceability across the waste management supply chain. - AI-Powered Predictive Waste Management
AI-driven predictive analytics can forecast waste generation trends, enabling businesses to proactively manage waste reduction strategies. - Robotics in Waste Sorting and Recycling
Robotics and automation are increasingly used in waste sorting facilities to enhance precision and efficiency in recycling processes. - Advanced Material Recovery Technologies
Innovations in material recovery are transforming the way waste is processed and repurposed. This reduces landfill waste and promotes circular economy principles by reintroducing recovered materials into production cycles. - Government and Corporate Policy Alignment
As ESG regulations tighten, businesses must align their waste management strategies with evolving government policies to ensure compliance and sustainability.
Conclusion
The future of ESG performance is inextricably linked to how organizations manage their waste and by embracing smart waste management technologies you have the tools you need to reduce your environmental impact, improve social responsibility, and strengthen corporate governance in ESG frameworks.
Sources
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). (2024). Global waste management outlook 2024. Retrieved February 6, 2025, from https://www.unep.org/resources/global-waste-management-outlook-2024
RTS. (n.d.). ESG guide: Part II. Retrieved February 6, 2025, from https://www.rts.com/resources/guides/esg-guide-part-ii/
Waste Dive. (2015, September 21). Talkin’ trash: Quotes from waste management, mayor of Baltimore, and more. Retrieved February 6, 2025, from https://www.wastedive.com/news/talkin-trash-quotes-from-waste-management-mayor-of-baltimore-and-more/408281/
RTS. (n.d.). What is a smart waste bin? Retrieved February 6, 2025, from https://www.rts.com/blog/what-is-a-smart-waste-bin/
RTS. (n.d.). Pello smart bin sensors. Retrieved February 6, 2025, from https://www.rts.com/pello-smart-bin-sensors/
RTS. (n.d.). Cycle reverse vending machine. Retrieved February 6, 2025, from https://www.rts.com/cycle-reverse-vending-machine/
RTS. (n.d.). Smart waste management technologies. Retrieved February 6, 2025, from https://www.rts.com/blog/smart-waste-management-technologies/
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI). (n.d.). Home page. Retrieved February 6, 2025, from https://www.globalreporting.org/
Financial Stability Board Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (FSB-TCFD). (n.d.). Home page. Retrieved February 6, 2025, from https://www.fsb-tcfd.org/

